0
0
What Happens During a Compressed Air Measurement & Audit?

Compressed air is a crucial component in many industries, powering tools, machinery, and production processes. However, inefficiencies in a compressed air system can lead to energy waste, increased costs, and reduced equipment performance.
Whether using a VSD air compressor or an oil-free air compressor, businesses must ensure their systems operate efficiently. To achieve this, companies conduct compressed air measurement & audit processes, which help identify inefficiencies and optimise performance. This guide provides a detailed overview of the key steps involved.
Understanding Compressed Air Audits
A compressed air audit is a systematic evaluation of a system’s performance and efficiency. It involves collecting data, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending improvements to enhance reliability and reduce energy consumption. The main objective is to optimise compressed air usage while lowering operational costs.
There are different levels of audits:
- Walk-through assessment – A basic inspection to identify obvious inefficiencies within the system.
- System assessment – A more detailed review incorporating essential measurements and performance analysis.
- Full system audit – A comprehensive study that includes in-depth data collection, leak detection, airflow analysis, and tailored recommendations for system optimisation.
Steps Involved in a Compressed Air Audit
1. Conducting a Site Survey
The audit begins with a detailed site survey, which includes:
- Documenting the environmental conditions and overall system layout.
- Identifying all system components, including compressors, dryers, filters, piping, and storage tanks.
- Understanding the specific processes and applications that use compressed air to determine actual demand.
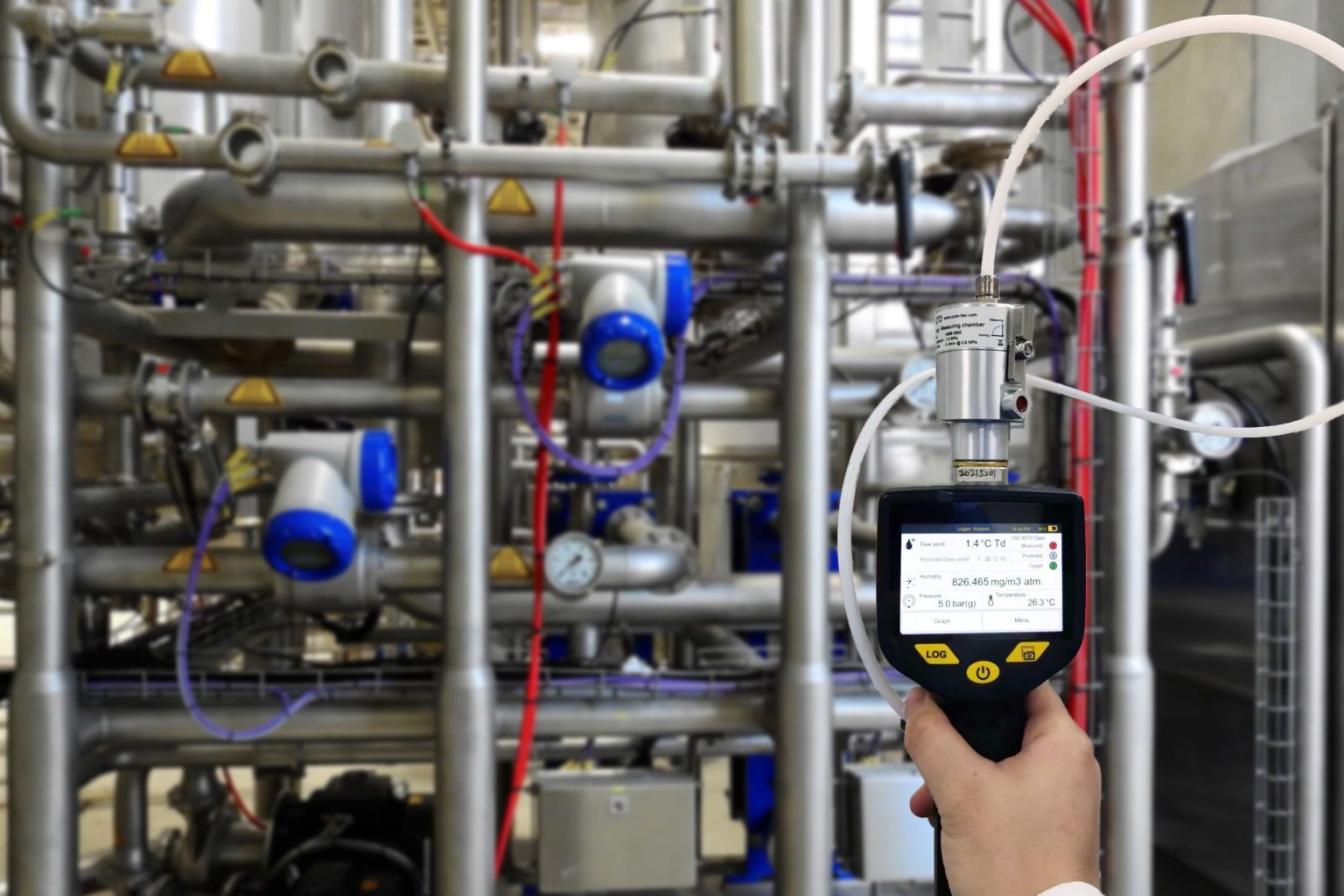
2. Measuring and Quantifying Energy Consumption
To determine system efficiency, auditors use specialised tools to measure key performance indicators such as:
- Power consumption (kW) – How much energy the system uses.
- Airflow (CFM – cubic feet per minute) – The amount of compressed air being generated and used.
- Pressure levels (PSI – pounds per square inch) – Ensuring pressure settings are appropriate and efficient.
- Leakage rate – Measuring how much air is lost due to leaks within the system.
By analysing these measurements, auditors calculate the specific power consumption (kW per 100 CFM) to determine overall system efficiency.
3. Detecting and Addressing Air Leaks
One of the leading causes of energy waste in compressed air systems is air leaks. Detecting and addressing leaks is crucial for maintaining efficiency. The process includes:
- Using ultrasonic leak detectors to locate leaks in pipes, fittings, and equipment.
- Measuring the volume of air lost and calculating the associated energy costs.
- Providing recommendations for repair and maintenance to prevent further air loss.
4. Evaluating System Dynamics and Pressure Levels
A well-functioning system should maintain stable pressure levels without unnecessary fluctuations. During the audit, experts:
- Analyse pressure drops across the system to identify inefficiencies.
- Ensure compressors operate within optimal pressure ranges to prevent over-pressurisation.
- Assess whether the system has adequate storage capacity to manage fluctuating demand effectively.
5. Reviewing Air Treatment and Quality
Compressed air quality is critical, particularly in industries where clean, dry air is essential. The audit includes:
- Assessing the performance of dryers, filters, and separators.
- Check for moisture, oil, or contaminants that may compromise air quality.
- Ensuring compliance with industry standards for compressed air purity and safety.
6. Analysing Piping and Distribution
The layout and condition of the compressed air distribution system significantly impact efficiency. Auditors examine:
- The design and structure of the piping network.
- Any restrictions, leaks, or improper pipe sizing that may cause pressure drops.
- Providing recommendations for layout improvements to enhance airflow and minimise energy losses.
7. Assessing Demand-Side Requirements
Understanding how compressed air is used on the demand side helps improve system performance. The audit focuses on:
- Evaluating the actual compressed air needs of various processes and applications.
- Identifying inappropriate or inefficient uses of compressed air.
- Suggesting demand-side control strategies to match air supply with actual demand and eliminate unnecessary consumption.
Partnering with Atom Drive for Optimal Compressed Air Solutions
A compressed air measurement & audit is essential for businesses looking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure reliable system performance. Whether you use a VSD air compressor or an oil-free air compressor, having a well-audited system can lead to significant energy savings and operational benefits. By following a structured audit process, companies can identify inefficiencies and implement solutions to optimise their compressed air systems.
At Atom Drive, we specialise in compressed air solutions, offering professional audits, system optimisation, and energy-saving strategies. Our experts help businesses maximise efficiency, lower energy consumption, and maintain high-performance compressed air systems.
If you want to enhance your system’s performance, contact Atom Drive today for a tailored compressed air audit that meets your operational needs.